Law Of Supply And Demand Graph Explained

The quantity of a commodity that is supplied in the market depends not only on the price obtainable for the commodity but also on potentially many other factors such as the prices of substitute products the production technology and the availability and cost of labour and other factors of production in basic economic analysis analyzing supply involves looking at the.
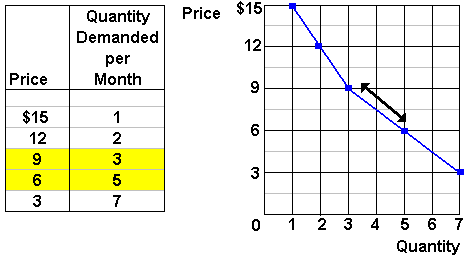
Law of supply and demand graph explained. Given these assumptions the law of demand is explained in terms of table 3 and figure 7. The above table shows that when the price of say orange is rs. Law of supply is a microeconomic law stating that all other factors being equal as the price of a good or service increases the quantity of goods or services offered by suppliers increases and. The law of demand states that if all other factors remain equal the higher the price of a good the less people will demand that good.
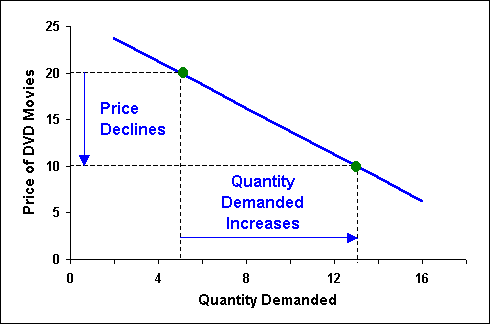
Just like the law of demand the law of supply highlights the quantities of goods that will be sold at a certain price in the market. If the price falls to rs 4 the demand increases to 200 units. The law of supply and demand is an economic theory that explains how supply and demand are related to each other and how that relationship affects the price of goods and services. The law of supply in the supply and demand curve.
5 per unit 100 units are de manded.







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Supplyrelationship-c0f71135bc884f4b8e5d063eed128b52.png)






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/IntroductiontoSupplyandDemand2_3-a0ab6cfec1444796a945c5aa0f181218.png)