Law Of Supply Graph Example

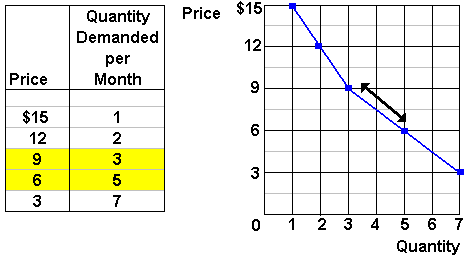
The law of demand expresses a relationship between the quantity demanded and its price.
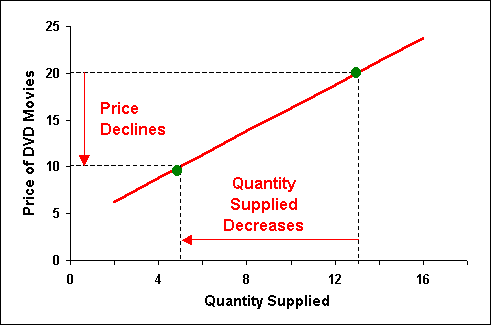
Law of supply graph example. This point is known as the equilibrium between supply and demand equilibrium prices and quantities can be used to model a broad range of markets and economic activities. It may be defined in marshall s words as the amount demanded increases with a fall in price and diminishes with a rise in price. The law of supply is the principle that an increase in price results in an increase in supply the law of demand is the principle that an increase in demand results in an increase in price. Law of supply is a microeconomic law stating that all other factors being equal as the price of a good or service increases the quantity of goods or services offered by suppliers increases and.
Corn crops are very plentiful over the course of the year and there is more corn than people would normally buy. Below are examples of the law of demand and how consumers react to prices as their utility or satisfaction changes. The following are illustrative examples of supply and demand. Supply schedule is a tabular presentation of various combinations of price and quantity supplied by the seller or producer during a period of time.
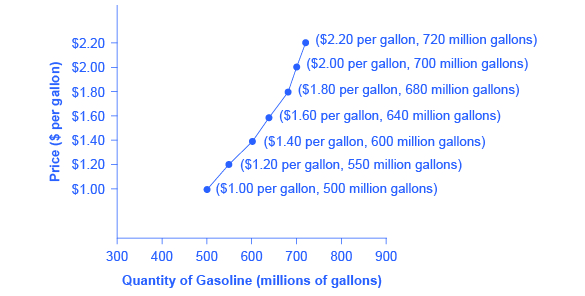
There is a drought and very few strawberries are available. This can be plotted as follows as an upward sloping supply curve in the graph below. The following are illustrative examples of the implications of these fundamental economic principles. To get rid of the excess supply farmers need to lower the price of corn and thus the price is driven down for everyone.
Assumptions of the law of demand 3. For example if a consumer is hungry and buys a slice of pizza. The quantity of a commodity that is supplied in the market depends not only on the price obtainable for the commodity but also on potentially many other factors such as the prices of substitute products the production technology and the availability and cost of labour and other factors of production in basic economic analysis analyzing supply involves looking at the. Demand can be represented either by a demand schedule a demand curve.
The law of supply can be explained with the help of supply schedule and supply curve as explained below. Introduction to the law of demand 2. Demand represents the quantity of a good which consumers are willing and able to buy at different prices. We can show the supply schedule through the following imaginary table.
Law of demand highlights the fact that people generally buy more of a good when its price is low and vice versa.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Supplyrelationship-c0f71135bc884f4b8e5d063eed128b52.png)